polarimeter optical rotation calculation|schematic diagram of polarimeter : suppliers rad/kg and molar optical rotatory power (α n) in m2 Andressa iniciou na atividade por acaso. Ela saiu da casa dos pais aos 15, após desavenças familiares (já resolvidas, segundo ela), e foi morar com a tia. No terreno havia um lava-jato de automóveis, e seu primeiro emprego acabou sendo lá, lavando carros. Certo dia, um caminhoneiro encostou o veículo na . Ver mais
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB11. 12. 13,690 fudendo rabuda gostosa FREE videos found on XVIDEOS for this search.
describe the features and operation of a simple polarimeter. calculate the specific rotation of a compound, given the relevant experimental data.Specific rotation equation, [α], is a fundamental property of chiral substances that is expressed as the angle to which the material causes polarized light to rotate at a particular temperature, wavelength, and concentration. The term for specific . Transfer the solution to the polarimeter tube within 30 minutes from the time the substance was dissolved and during this time interval maintain the solution at 25°. . Calculate the specific optical rotation using the .rad/kg and molar optical rotatory power (α n) in m2
It is the optical rotation for a given concentration, sample cell length, temperature, and wavelength. In turn, if you know the substance’s specific rotation, the concentration can be determined from the optical rotation . Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): The effect of path length on optical rotation. The longer the path of light through a solution of molecules, the more molecules will be encountered by the light, and the greater the optical rotation. The value of the optical rotation must be corrected for the length of the cell used to hold the sample.
Specific Rotation— The reference Specific rotation 781S in a monograph signifies that specific rotation is to be calculated from observed optical rotations in the Test solution obtained as directed therein. Unless otherwise directed, measurements of optical rotation are made at 589 nm at 25.Where a photoelectric polarimeter is used, a single measurement, corrected for the .The Lippich polarimeter is a more accurate variant. An improved method, based on an intervention of the Austrian physicist Ferdinand Franz Lippich in the late 19 th century, uses an additional optical element which introduces some rotation of the polarization direction for about half of the beam area after the polarizer. One can then not obtain .Angular rotation requires reporting the observed value of rotation but not calculating the specific rotation. Angular rotation is used for pure materials where there is no dilution. When reporting the specific rotation, the equations in General Chapter <781> are used to calculate the result of specific rotation.1. Preparing the Polarimeter. Turn on instrument and let it warm up for 10 min. Make sure instrument is set to "optical rotation" mode. Prepare a blank sample in the polarimeter cell (1.5 mL total sample volume, 1 dm in length) containing only CHCl 3.Make sure there are no air bubbles present.
Optical Rotation and Polarimeter by Dr. A. Amsavel - Download as a PDF or view online for free . Concentration of the sample, but SOR will not change, since concentration is consider in the calculation. 2. Wavelength of light passing through the sample. Angle of rotation and wavelength tend to be inversely proportional 3. Temperature of the .
why polarimeter is used
Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): The effect of path length on optical rotation. The longer the path of light through a solution of molecules, the more molecules will be encountered by the light, and the greater the optical rotation. The value of the optical rotation must be corrected for the length of the cell used to hold the sample.The value of the optical rotation must be corrected for the length of the cell used to hold the sample. In summary: \[[\alpha] = \frac{\alpha}{c \times l} \nonumber\] a is the measured optical rotation. c is the sample concentration in grams per deciliter (1 dL = 10 mL). That is, c = m / V (m = mass in g, V = volume in dL). l is the cell length . To calculate specific rotation, we use a device called a polarimeter, which allows us to find the rotation of plane-polarized light. This calculation is used in the specific rotation equation to . The "optical purity" is a comparison of the optical rotation of a pure sample of unknown stereochemistry versus the optical rotation of a sample of pure enantiomer. It is expressed as a percentage. If the sample only rotates plane-polarized light half as much as expected, the optical purity is 50%.
The automatic polarimeter calculates the optical rotation of the sample based on the change in the angle of the analyzer needed to restore the light intensity to its original level. . and calculate results without manual intervention. The automation of these processes enhances efficiency, precision, and the overall reliability of optical .
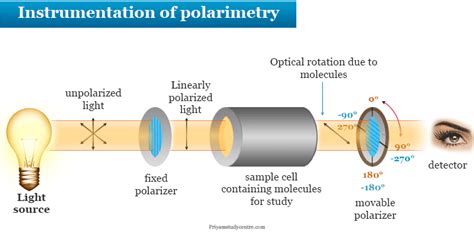
The plane of polarization can be determined by an instrument called a polarimeter, shown in the diagram below. Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Operating principle of an optical polarimeter. 1. Light source 2. Unpolarized light 3. Linear polarizer 4. Linearly polarized light 5. Sample tube containing molecules under study 6. Optical rotation due to .
Again, we know that the S enantiomer is in excess because the specific rotation of this isomer (enantiomer) is +23.1 and the sample has a positive optical rotation. To find the enantiomeric excess, we can now plug in the numbers .
which lamp used in polarimeter
what does a polarimeter measure
schematic diagram of polarimeter
Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Operating principle of an optical polarimeter. 1. Light source 2. Unpolarized light 3. Linear polarizer 4. Linearly polarized light 5. Sample tube containing molecules under study 6. Optical rotation due to molecules .Polarimeters are essential instruments for analyzing the optical properties of substances. These devices measure the rotation of polarized light as it passes through a sample, providing valuable information about the chemical composition and concentration of the material being analyzed. Polarimeters are widely used in a variety of fields, including chemistry, biology, .
Source Video: Polarimeter Measurement Procedures to Determine Optical Rotation / Specific Rotation Video Transcript from the Rudolph Research Video Library. This video covers how to fill cells and make a (Optical Rotation and Specific Rotation) measurements using a Rudolph polarimeter equipped with the exclusive and patented Temptrol heating and cooling system.
The polarimeter is a fully automatic research-grade instrument that calculates the optical rotation at the push of a button, with an accuracy of ±0.0013° and a precision of ±0.0028 .
1. Louis Pasteur And The Discovery Of “Enantiomers” In our last post on optical rotation (See post: Optical Rotation, Optical Activity, and Specific Rotation) we saw that when Louis Pasteur crystallized a salt of a compound then known as “racemic acid” he discovered that it formed two different types of crystals.When redissolved in water, one set of crystals rotated . Optical activity is measured by a polarimeter, and is dependent on several factors: concentration of the sample, temperature, length of the sample tube or cell, and wavelength of the light passing through the sample. Rotation is given in +/- degrees, depending on whether the sample has d- (positive) or l- (negative) enantiomers. The standard . The polarimeter. The optical rotation is measured with an instrument called a polarimeter. In this apparatus, polarized light of known plane is emitted on one side of the instrument. . A calculation then allows to correct the raw reading and express the true optical rotation for the pure substance (figure 4). Figure 4. Interface of the .
These labs, once bustling with activity, are now forgotten. Let's take a look at some of these lost centers of optical rotation. 1. Carl Zeiss Optical Workshop. Carl Zeiss, a name synonymous with optical excellence, had a workshop in Jena that played a crucial role in developing polarimeters. This workshop was a hub for innovation and precision.] By definition, a solution containing 26.000 g sucrose in 100.000 cm 3 at 20°C in a 200 mm pol tube, will have an optical rotation of 34.626° at 589.44 nm ( Player et al., 2000).Proteins are removed in the procedure with stannic chloride-phosphotungstic acid. The resulting filtered solution's optical rotation is measured in the polarimeter and used to calculate percent starch; a similar optical procedure uses hydrochloric acid and a saturated lead solution.
instron tensile compression tester model 4481
instron tensile compression tester model 4481 diagrams
webGet the free Microsoft 365 mobile app. Collaborate for free with online versions of Microsoft Word, PowerPoint, Excel, and OneNote. Save documents, workbooks, and presentations online, in OneDrive. Share .
polarimeter optical rotation calculation|schematic diagram of polarimeter